Unicast / Broadcast / Multicast
Frames and Their Destinations
Frames are usually sent from one specific device to another.
Sometimes a frame is sent to every device on the LAN.
And occasionally, a frame is sent only to a selected group of subscribers.
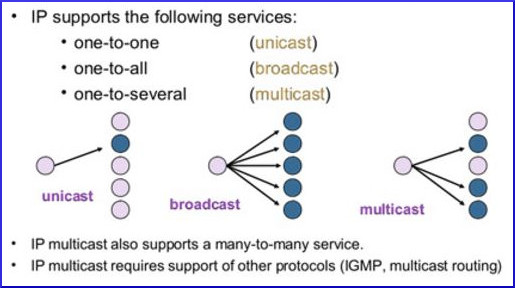
For these three types of network traffic, we use the following names:
UNICAST: A message sent to one single destination.
BROADCAST: A message sent to everyone on the network.
MULTICAST: A message sent to a group of subscribers (only the devices that have joined that group).
The destination is always an address.
There are two types of addresses: MAC-address and IP-address.
MAC address
A MAC address looks like this:
74:d4:35:80:b4:6c
It consists of 6 hexadecimal numbers, each with 2 digits, separated by colons.
IP address
An IP address looks like this:
10.0.1.254
It consists of 4 decimal numbers (each between 0 and 255), separated by dots.
Broadcast addresses
- The MAC broadcast is always the same:
ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff - The IPv4 broadcast must be calculated for each network.
An IPv4 broadcast address is the LAST address of a given network. To find the last address of a network we need to have a netmask
example of a calculation of a netID and a netBC for 192.168.23.0/24
- Network: 192.168.23.0/24
- Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
a /24 means: - First 24 bits = network part
- Last 8 bits = host part
So we can see it like this: - Network part: 192.168.23
- Host part: last number: (0–255)
- NetID (network address)
For the NetID, we keep the network part and set the host part to 0.- Network part: 192.168.23
- Host part: 0
- NET-id =192.168.23.0 (this is the network address. It identifies the network itself)
- NetBC (broadcast address)
For the broadcast address, we keep the same network part,
but set the host part to 255 (last address / all bits = 1).- Network part: 192.168.23
- Host part: 255
- Network ID: 192.168.23.0 (first address of this network - see above)
- Broadcast address: 192.168.23.255 (last address of this network)
This is the address used to send a message to all hosts in the 192.168.23.0/24 network.
- Summary
- NetID: 192.168.23.0 (net identifier)
- NetBC: 192.168.23.255 (net broadcast)
- binary calculation
Address: 192.168.23.0 11000000.10101000.00010111 .00000000 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 = 24 11111111.11111111.11111111 .00000000 Wildcard: 0.0.0.255 00000000.00000000.00000000 .11111111 (ospf value) => Network: 192.168.23.0/24 11000000.10101000.00010111 .00000000 (Class C) Broadcast: 192.168.23.255 11000000.10101000.00010111 .11111111 HostMin: 192.168.23.1 11000000.10101000.00010111 .00000001 (first useable address) HostMax: 192.168.23.254 11000000.10101000.00010111 .11111110 (last useable address) Hosts/Net: 254 (Private ip-address)